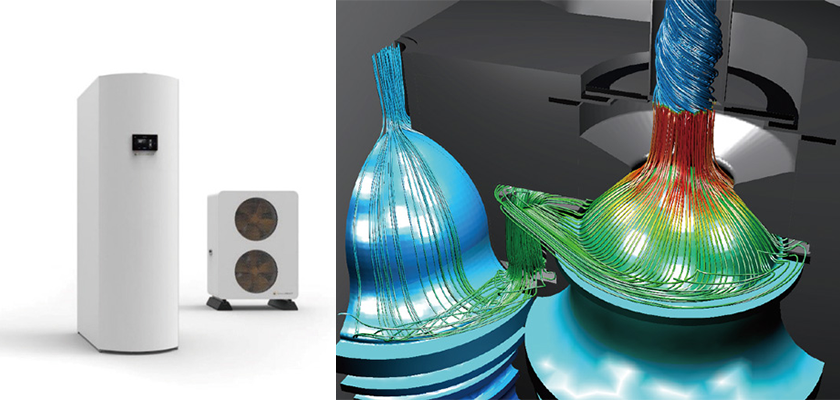
scFLOW / scFAST
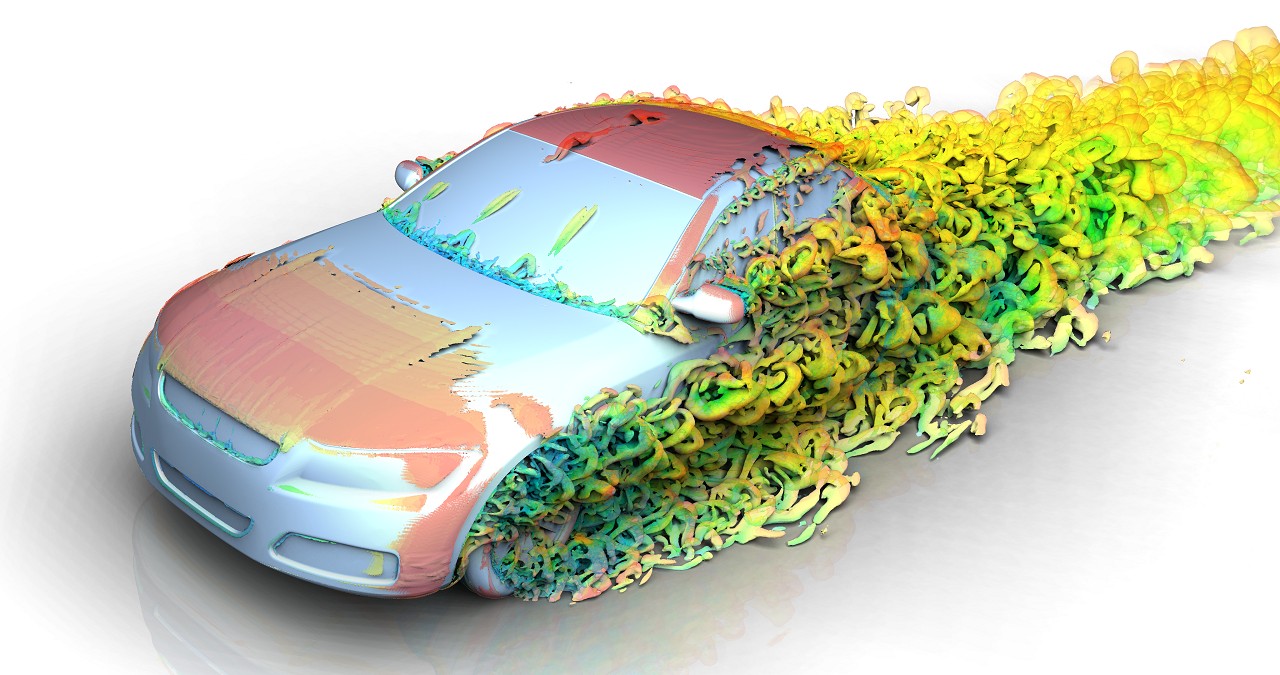
Overview
SC/Tetra has been characterized by sophisticated mesh generation function, high speed computing capability, and user-friendly features throughout the operation. As its advanced version, scFLOW has been released. It is equipped with more stable Solver that achieves calculation speed three times faster (at maximum) than before, and new Preprocessor that helps entry-level users build complicated models and highquality mesh. scFLOW, the new generation software, keeps on evolving. scFAST is GPU-native CFD solver, which offers significant speed increases compared to HPC CPU-powered platforms, especially when dealing with large-scale models.
Program Structure
Simplification of Preprocessor operations
From the CAD data to analysis mesh data, the required operations are grossly simplified compared to before. The conservation of assembly information and the settings of conditions on the parts bring the sense of continuity from the CAD operations and reduce the operational burden of the users.
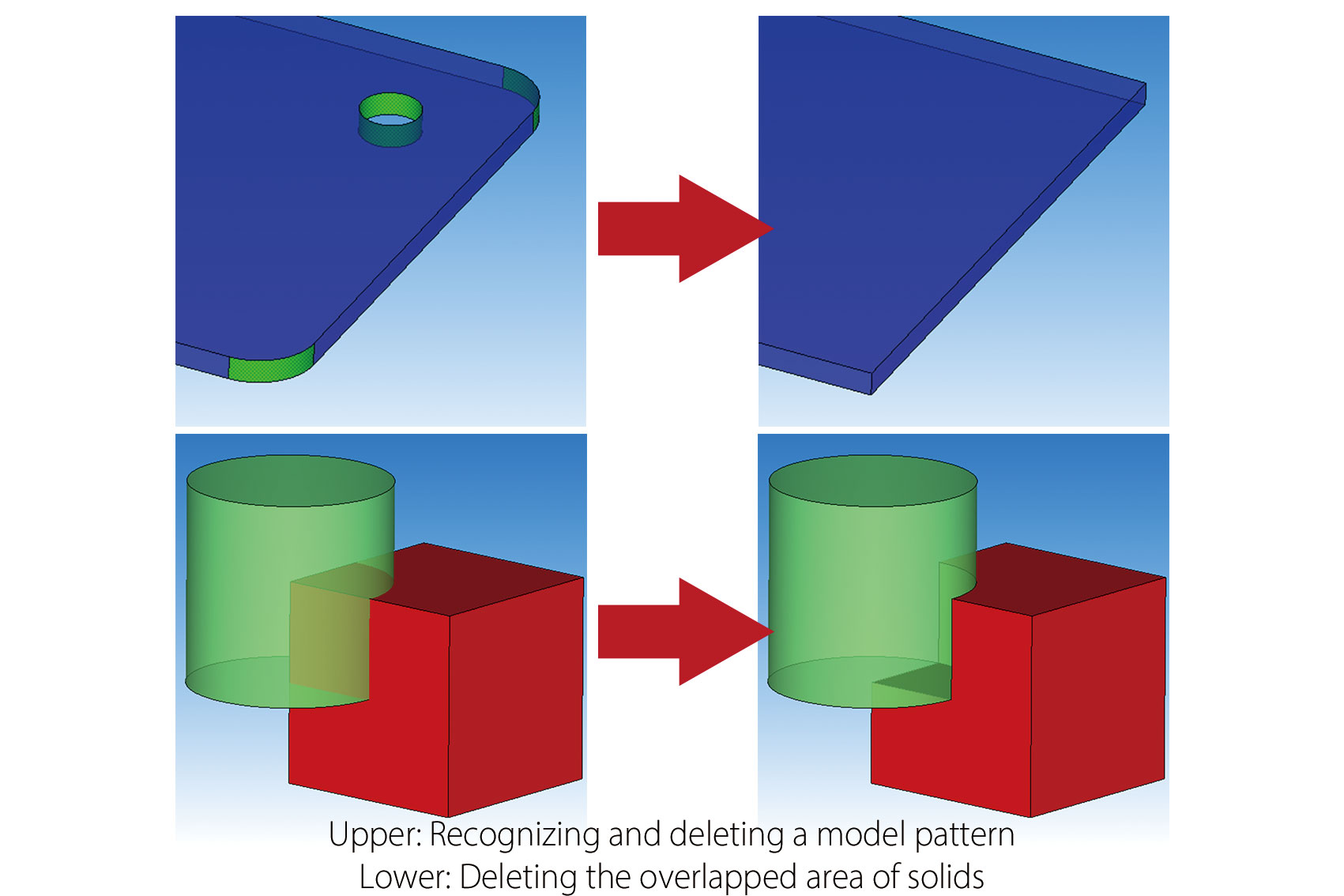
Modifying CAD data
When CAD data to be used for simulation has a problem, the data can be modified with Preprocessor. Boundary conditions can be set based on the part names and color information set in the CAD data. When some regions are missing in the model, shapes such as cuboids and cylinders can be added.
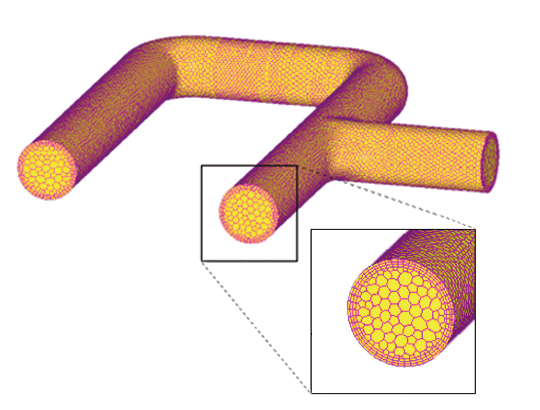
Polyhedral mesher
Using polyhedral mesh elements improves stability and calculation accuracy of cell-centered solver. In scFLOWpre, mesh can be generated according to the target number of mesh elements and automatically refined near wall area. The automatic mesher function also enables users to specify mesh refinement level of each part and region.
Voxel Fitting Mesher
The function can analyze passive translation and rotation of an object receiving a fluid force. A moving object is assumed to be a rigid body. Its movement whose maximum degree of freedom is six (3D translation + 3D rotation) can be solved. The function can simulate driftwood which is flowed by a force from water flow.
Mesh-adaptation analysis
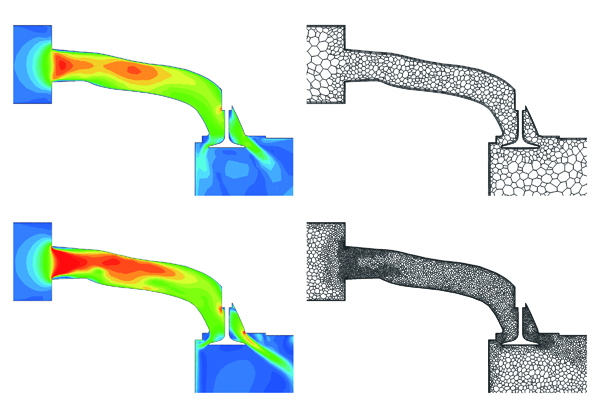
With this function, mesh will be automatically refined where a flow or pressure changes greatly in a steady-state analysis. After the calculation in Solver is completed, Preprocessor automatically launches and executes gridding and meshing based on the calculation result. By specifying the target number of elements, coarse mesh is generated first and the mesh is automatically refined to be appropriate for the calculation. The function is useful for an analysis of flows in a tube with a complicated shape.
Dynamic Adaptive Mesh Refinement
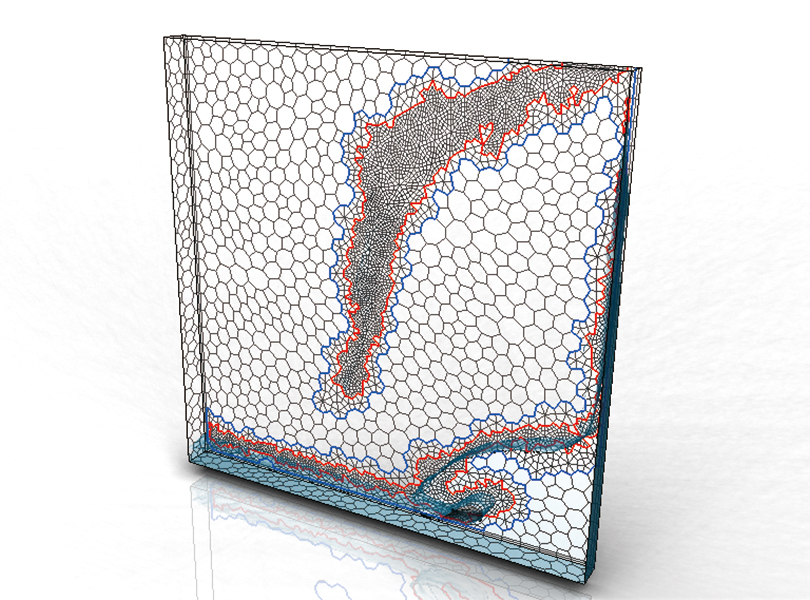
Dynamic Adaptive Mesh Refinement allows dynamic mesh splitting and merging during solver execution for unsteady analysis. By adjusting mesh resolution based on the importance each cycle, it enables high-fidelity simulations. This feature is invaluable for analyzing free surfaces and vortex tracking, capturing complex fluid phenomena with precision.
Stabilization of calculation
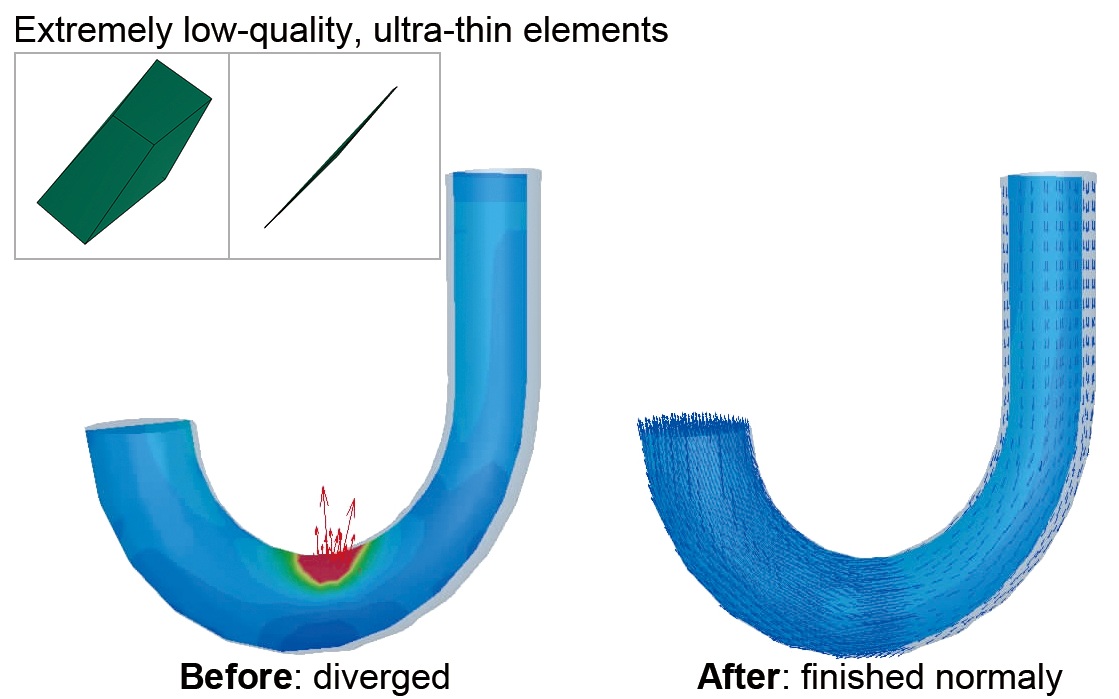
Even for mesh data with elements of extremely low quality, the calculation can be stabilized by the automatic processing to avoid divergence. This function helps Solver be more robust.
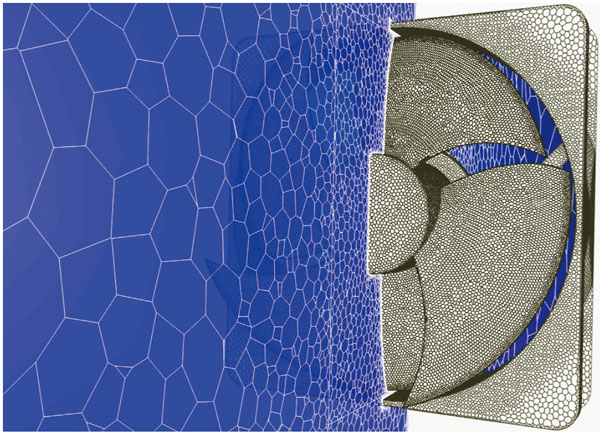
Discontinuous mesh
Flow with object motion can be calculated, including rotation of fans and turbines, and crossing travel of automobiles or trains (translation). The function enables an analysis with consideration on shear heating between rotor and pad in a disk brake. The function also makes it possible to analyze a combination of rotation and translation such as a piston pump.
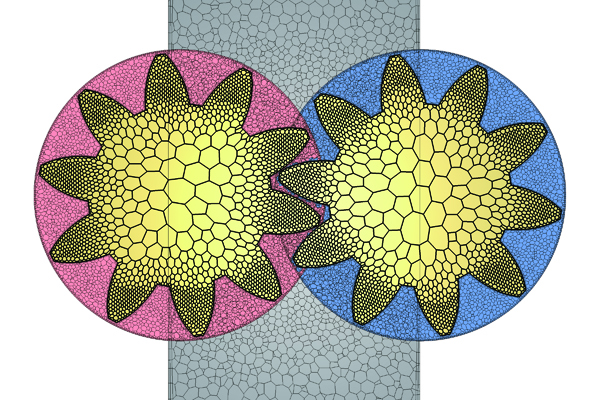
Overset mesh
Free movement of regions, that cannot be analyzed using existing functions such as stretching or rotating elements, can now be simulated by overlapping mesh elements for stationary and moving regions. This function supports an overlap of multiple moving regions, a contact between objects, and a 6-degree-of-freedom motion of rigid bodies. This is useful to analyze opening and closing of a valve of an engine port or a gear pump where gears engage with each other.
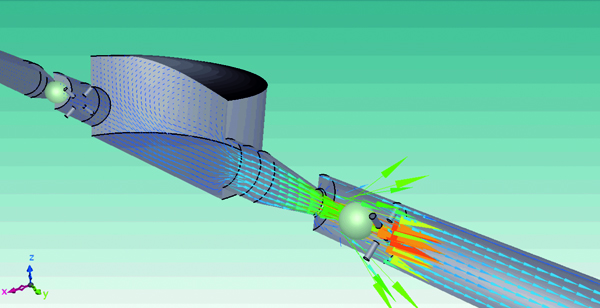
6-degree-of-freedom motion (6DOF)
Passive translation and rotation of a rigid body receiving a fluid force can be analyzed. With the function, the user can analyze a ball valve with consideration of the elasticity of the spring (1D translation), and paper airplane with consideration of 6-degree-of-freedom rigid-body motion (3D translation + 3D rotation). In addition, the function is applied to analyses of check valves, wind power generators, and blades of wave power generators.
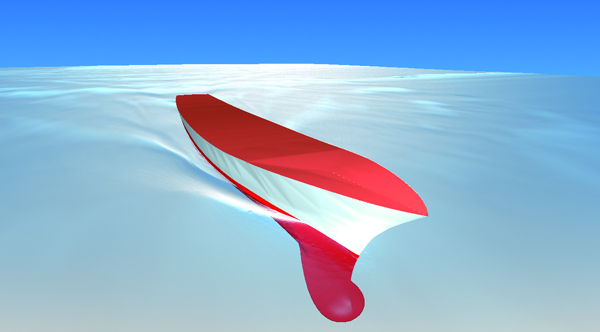
Free surface (steady-state / transient)
The shape of an interface between a gas and a liquid can be simulated. Calculations by VOF method (new method: FIRM) are fast and accurate, and functions including moving boundary, overset mesh, and particle tracking can be used in combination. Because a phenomenon where the phase interface becomes stable can be analyzed in a steady-state calculation, the result can be obtained in a shorter time than before.
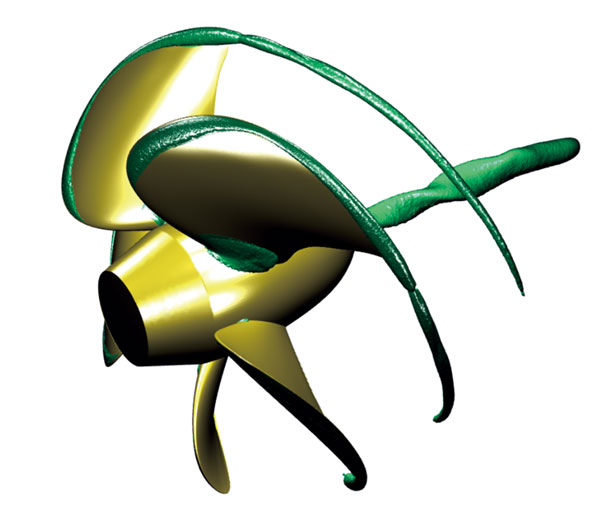

Cavitation
This function enables simulation of a vaporization phenomenon called cavitation, which is caused at an area where pressure of a liquid becomes lower than in the surrounding area, such as with a propeller rotating at a high speed under water. The occurrence of cavitation can be predicted by applying the cavitation model based on the pressure values. The software also supports problems caused by cavitation such as erosion.
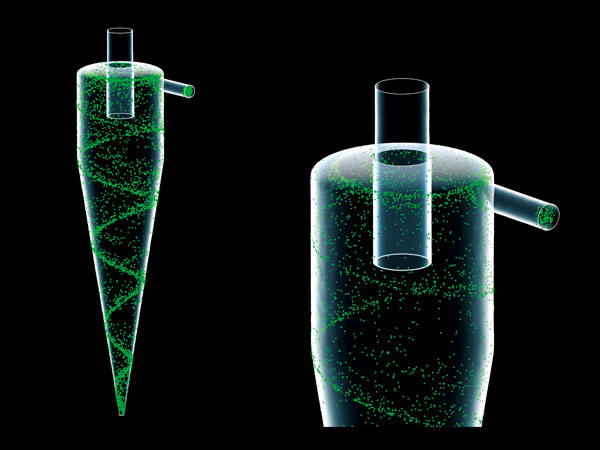
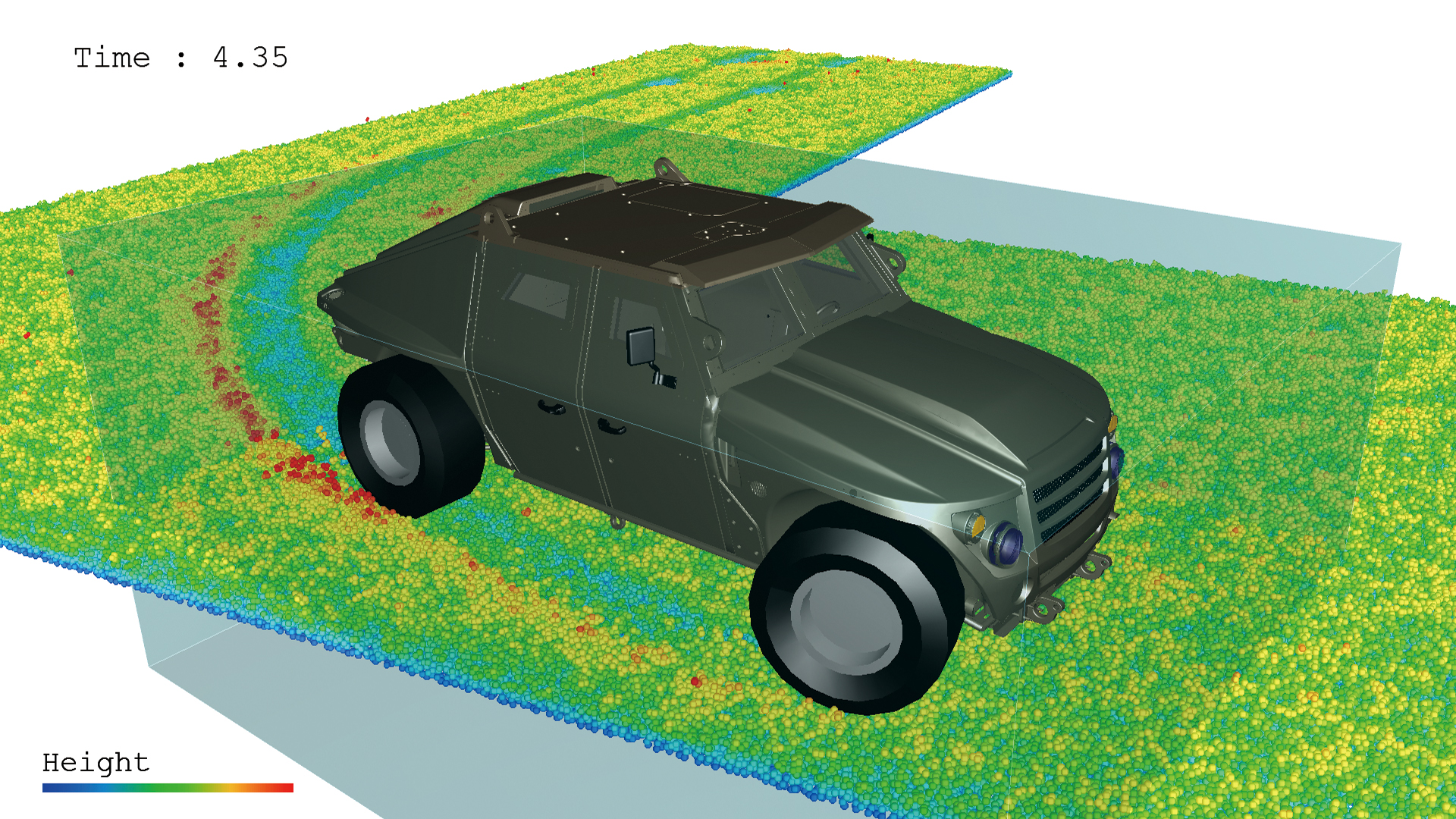
Particle tracking
Particle tracking function enables analyzing behavior of particles in flow. When analyzing small particles that follow the fluids movement (such as steam and dust), marker particle function can be used to evaluate particles in flow that change over time, which assumes that particle movement is in accordance with fluid velocity.

Discrete Element Method (DEM)
scFLOW's DEM feature simulates particle motion and fluid interaction, modeling collisions and friction accurately. It enhances process optimization across industries, offering a high-precision, integrated CFD analysis environment.
Evaporation/Condensation
Free surface analysis function (VOF method) of this software can simulate phase change between gas and liquid, such as evaporation and condensation. By considering phase change, not only simple heat conduction but also heat transfer from latent heat can be calculated. For example, this method can be applied to internal flow simulations for heat transfer devices such as heat pipes, in which a refrigerant liquid changes to vapor by absorbing heat from an outer region.
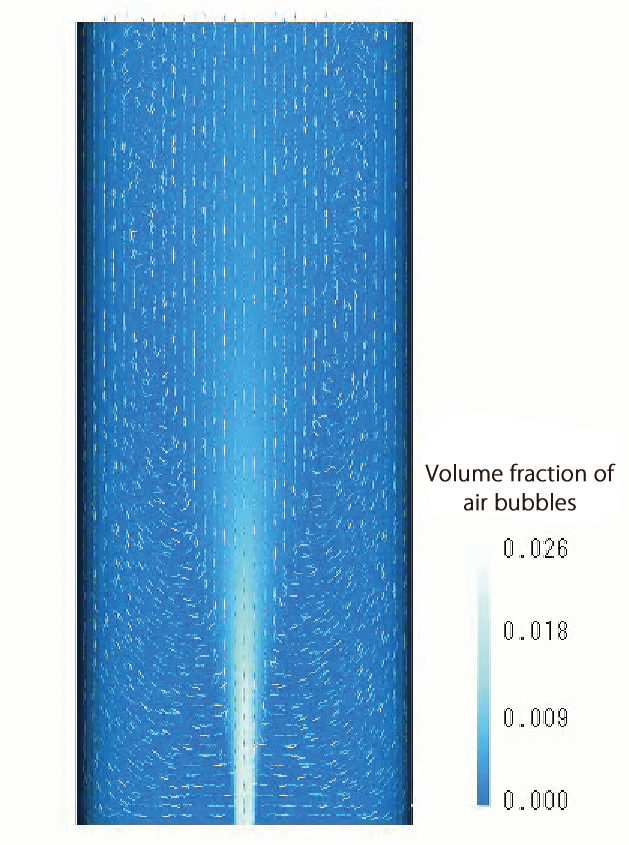

Dispersed multi-phase flow
This function can simulate flows containing many bubbles, droplets, or particles (dispersed phase), which are difficult to be analyzed using free surface. This function is a multi-fluid model that can predict volume fraction distribution and velocity distribution of each phase by solving the governing equation under the assumption that the dispersed phase is a fluid (continuous phase). The function is useful to analyze the bubble jet effect and aeration tanks.
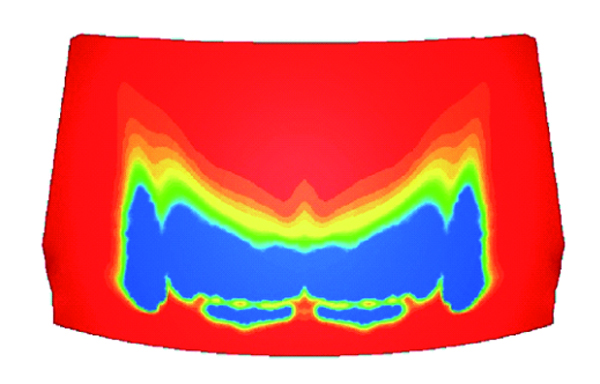
Humidity dew condensation
The amount of dew condensation on an object surface can be calculated from the surface temperature and water vapor in the air. You can output the amount of dew condensation per unit time in a steady-state analysis and the accumulated dew condensation in a transient analysis. Evaporation from a surface where dew condensation occurs can be calculated simultaneously, and this is useful for an analysis of a windshield defroster.
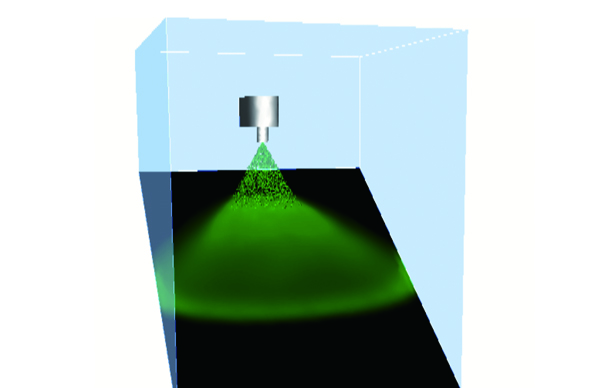
Liquid film model
The liquid film model is an extended function of the particle tracking function. By using the model, you the user can simulate the phenomenon that liquid particles change to a liquid film (water on a wall) when they reaching on the a wall. A liquid film on a wall flows with the influence of gravity and a gas-phase flowdown depending on an angle of the wall and collects in at a certain position. The analysis results are output as the thickness of a liquid film.
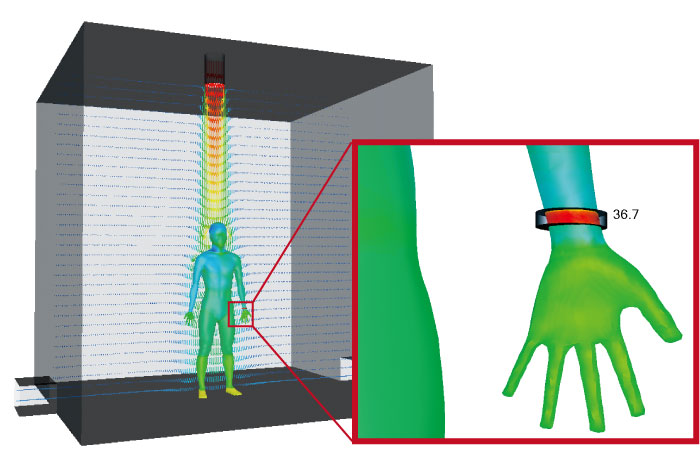
Thermoregulation-model (JOS)
Combination use of the thermoregulation-model (JOS) and a fluid analysis enables analyses of the surface temperature of a human body under a certain thermal environment. It can also be used to analyze temperature and humidity changes in the surrounding environment of a human body. The user can consider age, clothes, and physiological phenomena of the human body such as heat transfer by blood flow in addition to the surrounding environment of a human body such as temperature and velocity.
* JOS-2, and JOS-3, developed by the Tanabe laboratory at Waseda University, et al., are introduced for the thermoregulation model
Battery Thermal Management & Safety
Thermal Management: Equivalent circuit model brings you fast and accurate thermal calculation while P2D model adds details based on Lithium ion transport inside the cell.
Battery Safety: Semi-Empirical thermal runaway model is a fast and accurate thermal runaway model based on ARC experiment data. The Kinetics-Driven thermal runaway model adds details on thermal runaway analysis with calculation of reaction rate equations.
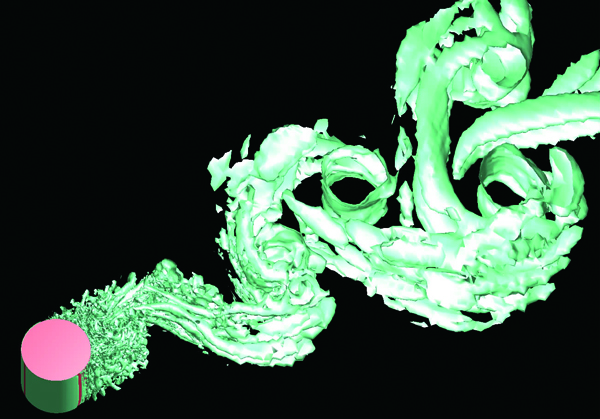
LES
LES is one of the turbulent flow models. It models eddies smaller than the mesh element in size and directly calculates other eddies. Although calculation load is large, LES enables simulations closer to real phenomena. LES is often used in noise analyses, significantly affected by time variation, to simulate the behavior of small eddies. The user can use the hybrid model with RANS, a turbulent model of small calculation load.
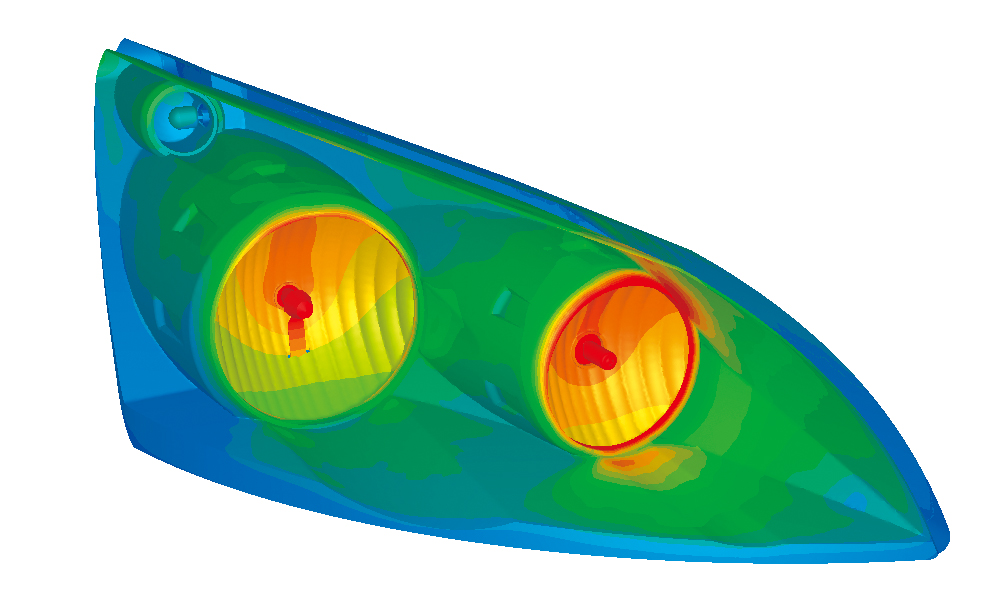
Radiation
Heat transfer by infrared-ray radiation can be considered by setting emissivity and temperature difference between objects. The user can choose VF (view factor) method or FLUX method as a calculation method. The user can also consider wavelength dependence, transmission, absorption, refraction, diffusion, and reflection of radiation. In FLUX method, the user can also consider directionality.
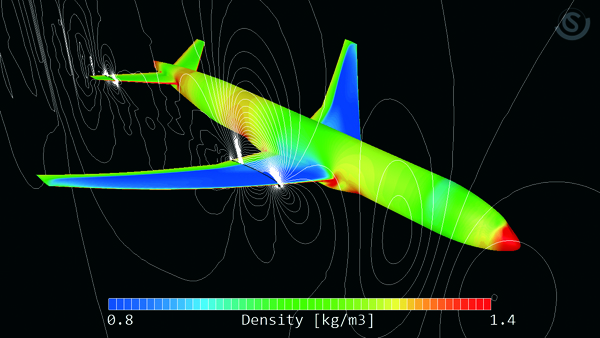
Compressible fluid
The software can analyze phenomena such as supersonic flow and significant expansion/contraction of volume. For a compressible fluid, both the pressure-based and the density-based Solvers can be used. The density-based Solver keeps the calculation stable even with high Mach number. You can select either Solver depending on the analysis target and phenomenon.
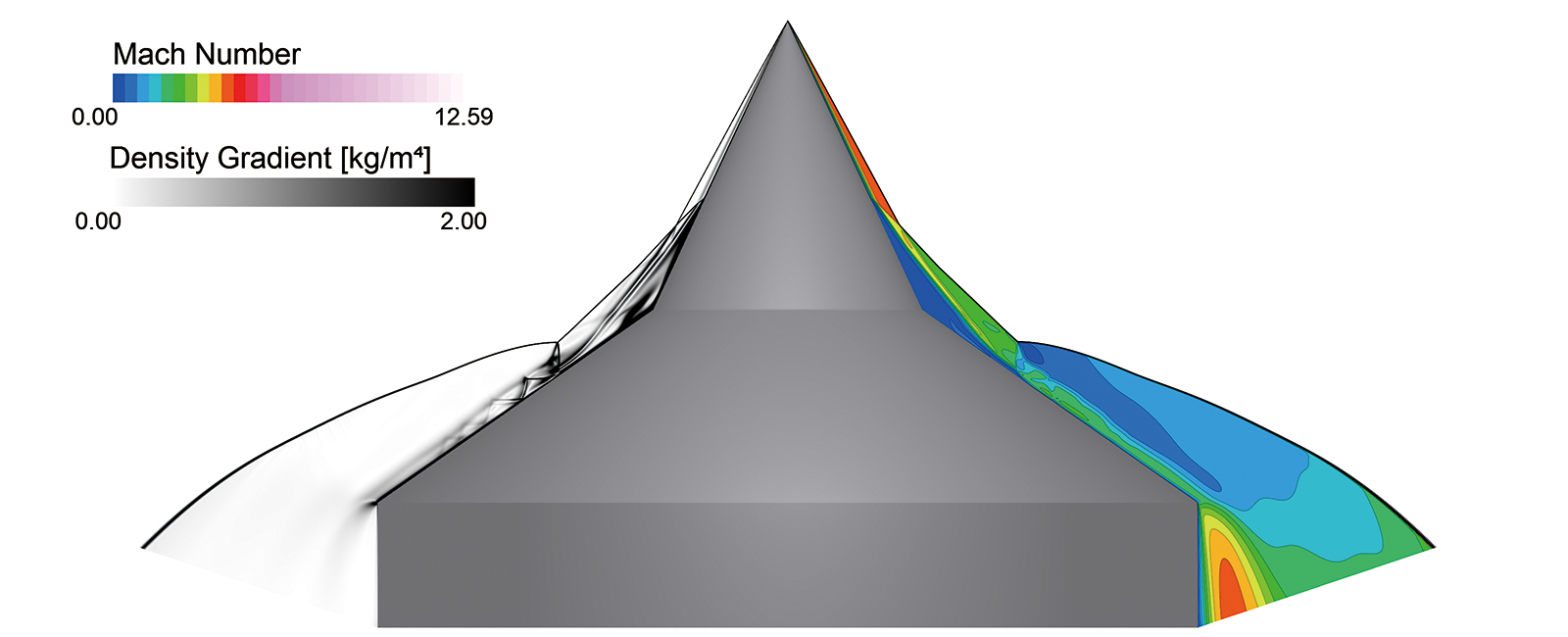
Hypersonic solver
The Hypersonic Solver in scFLOW extends the density-based solver for high-speed flows requiring advanced physics. It supports non-equilibrium thermodynamics and chemical reactions in air, enabling accurate predictions in hypersonic regimes, above Mach 5. This solver models high-temperature and high-speed phenomena beyond ideal gases, ensuring robust and precise analysis even at high Mach numbers.
* A separate license is required to use this feature.
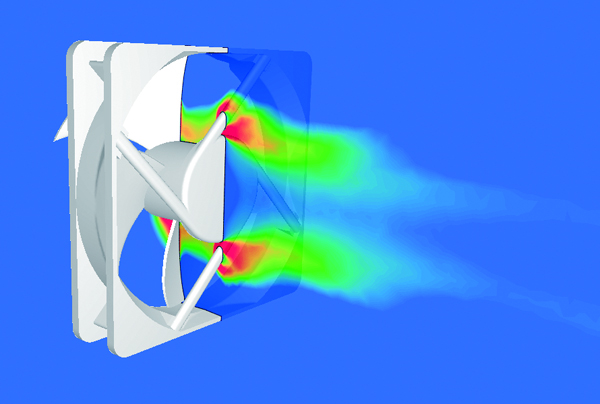
Aerodynamic noise analysis
Sound caused by pressure oscillation of a fluid, such as wind noise, and sound caused by resonance can be predicted. The calculation can be performed accurately by using LES. The frequency of aerodynamic noise can also be analyzed using the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) method from the CFD analysis result.
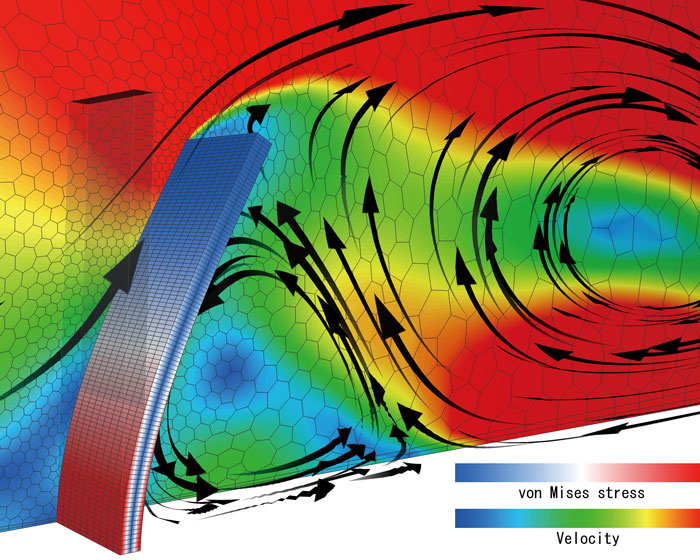
Fluid-structure interaction
This option is used for two-way FSI (fluid-structure interaction) with structural analysis software. With this option, not only rigid bodies but also elastic bodies can be treated. Deformation of an object caused by a fluid force and the change of fluid caused by the deformation can be analyzed.
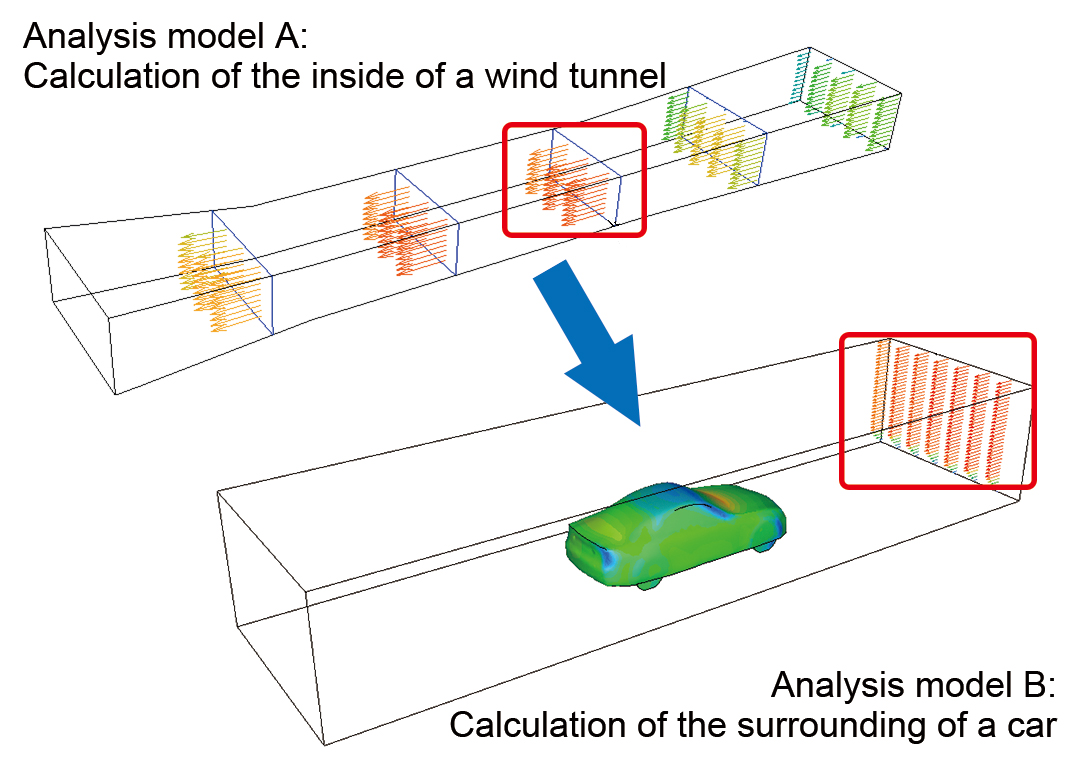
Mapping
When a target phenomenon is in a small range and the phenomenon is affected by a wide range of its surrounding area, analysis results of the surrounding area can be used for an analysis of the target phenomenon as boundary conditions to decrease the calculation load.
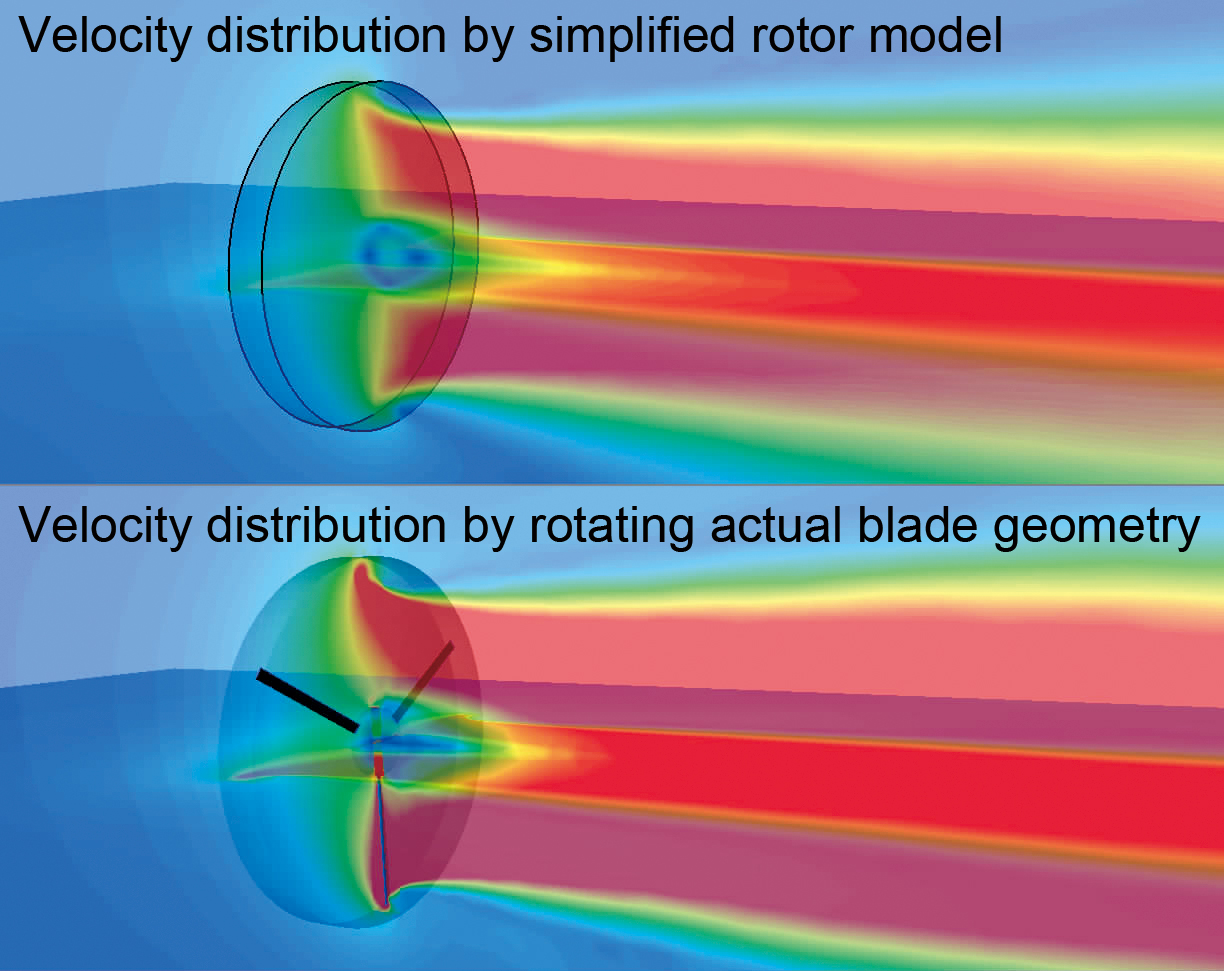
Fan model (rotating blades)
With this model, an average flow field around rotating blades can be simulated only by entering characteristic properties regardless of real shapes of fans or propellers. The user can use the non-dimensional swirl coefficient model, the simplified propeller model, and the simplified rotor model. This model is useful to analyze axial-flow windmills and waterwheels.
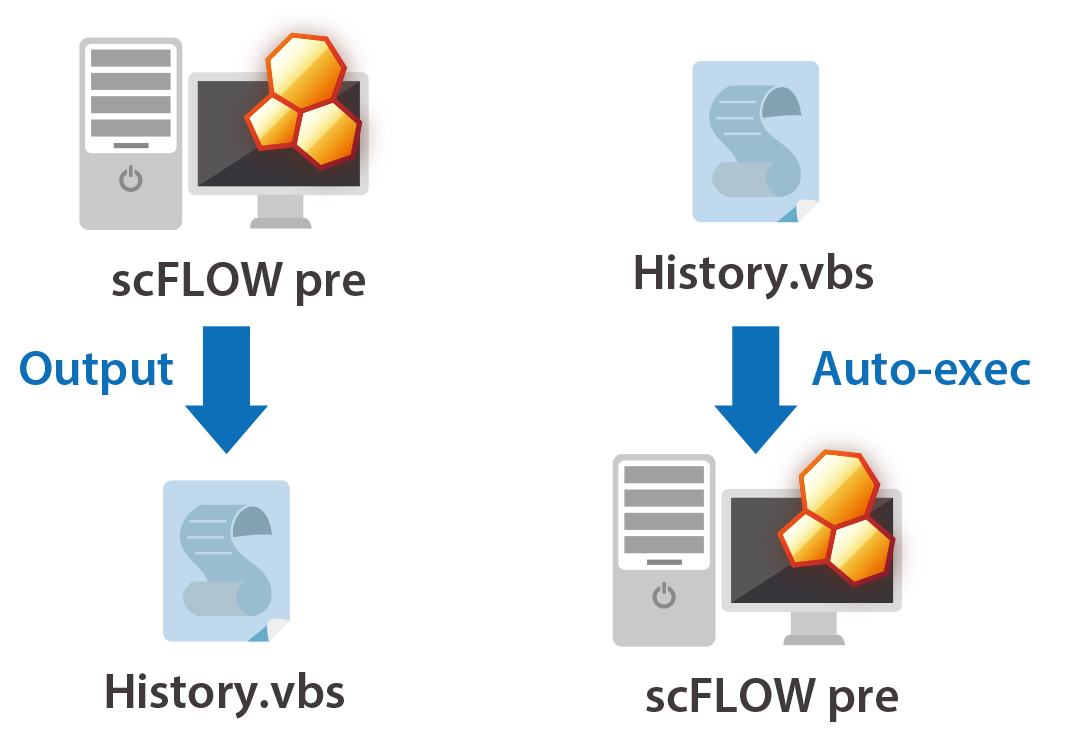
Operation logging by VB interface
The operations in Preprocessor can be saved as a log file using the VB interface. Making the user scripting unnecessary, this makes the construction of an automated system affordable in a short period of time based on the files storing the operation logs.
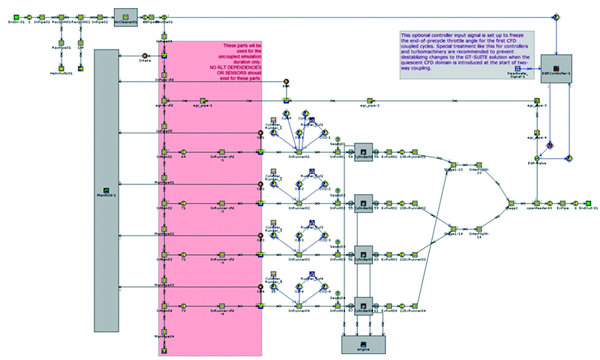
Coupled analysis with GT-SUITE
Coupled analysis with GT-SUITE is available. The entire flow in an intake and exhaust system is calculated with GT-SUITE and small flows of each part are interpolated with scFLOW or SC/Tetra. This will enhance calculation accuracy of the whole system.
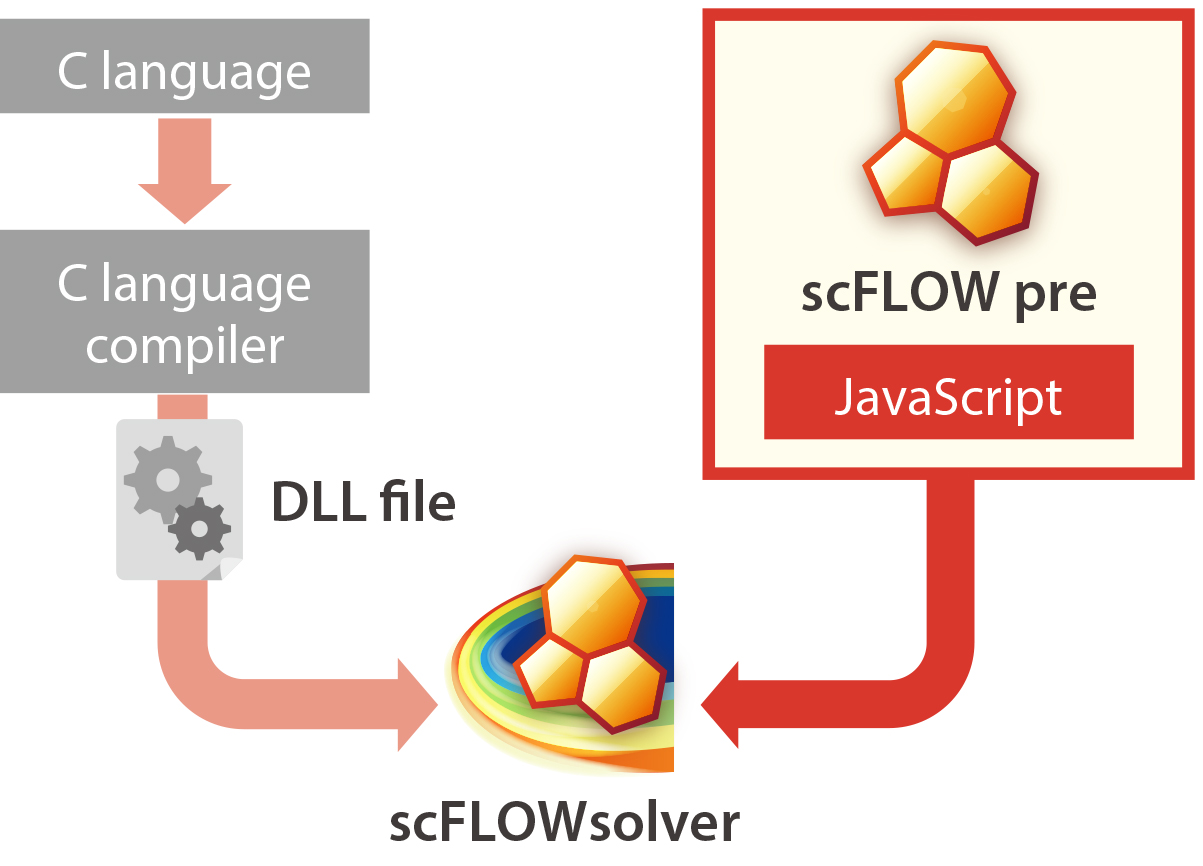
Script functions
Before, complicated settings, including time-/coordinate-dependent material properties or boundary conditions, required a coding and compilation of user-defined function in C language. With the script functions, compilation is not required. Functions can be written in Preprocessor based on JavaScript.
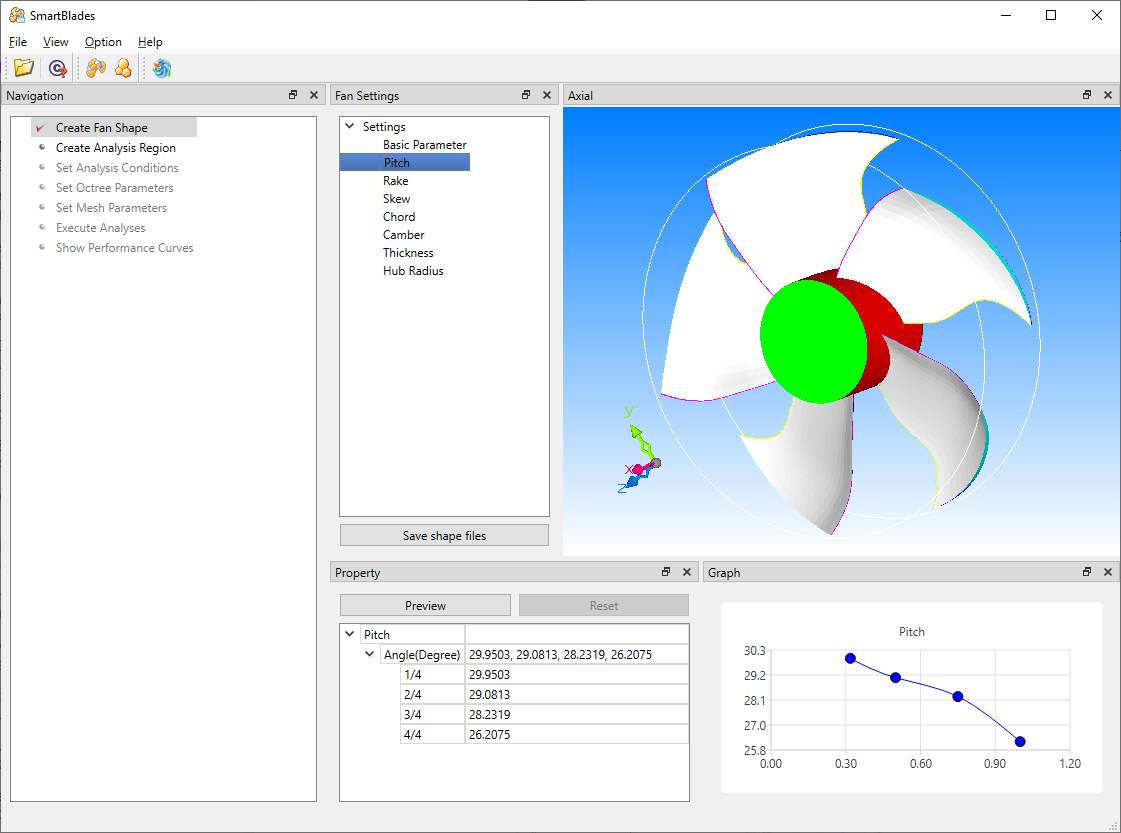
SmartBlades
This function is useful for analyzing the shape of a fan automatically throughout creating the shape of a fan (CAD data), calculating the flow, and post-processing. The shape of a fan can be created easily by specifying parameters including the number of blades, fan diameter, rake angle, and skew angle.



