Reynolds number
Reynolds number
Reynolds number is a dimensionless number representing the ratio of inertia force and viscous force. It can be expressed with the following equation:
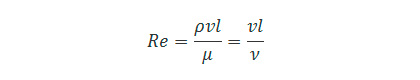
where;
Re : Reynolds number
l : Characteristic length [m]
v : Characteristic velocity [m/s]
ρ : Fluid density [kg/m3]
μ : Viscosity coefficient of fluid [Pa・s]
ν : Kinematic viscosity coefficient of fluid [m2/s]
Denominator of Reynolds number represents viscous force, and numerator the inertia force. Reynolds number is low when viscous force is dominant, and the flow becomes laminar. On the other hand, Reynolds number is high when inertia force is dominant, and the flow becomes turbulent.
Reynolds number is named after a British physicist Osbourne Reynolds.
