Navier-Stokes equations
Navier-Stokes equations
Navier-Stokes equations describe the conservation of fluid momentum
For example, the equations for an incompressible Newtonian fluid can be expressed as follows.
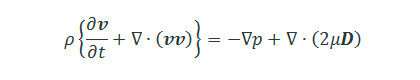
v : Flow velocity
t : Time
ρ : Density
p : Pressure
μ : Viscosity coefficient
Starting from left the terms are called time, convective (or advection), pressure, and viscosity (or diffusion) terms, respectively.
Navier-Stokes is named after the French physicist Claude Louis Marie Henri Navier and the Irish physicist George Gabriel Stokes.
